Taking care of the environment falls upon each of our shoulders. Even a small step towards green living can positively impact our ecosystem. Recycling organic waste into compost is one such step that can benefit our beloved planet.

Image credit:Mary Jane Duford
Table of ContentsWhat is Composting, in Simple Words?Compost MeaningWhy You Should Consider Composting of Waste: A Bouquet of BenefitsReduces Methane EmissionsEnriches Soil and Lessens ErosionConserves WaterWhat Can You Compost?How to Compost at HomeCompost IngredientsTemperatureSize and LocationSteps for Backyard CompostingTypes of Compost BinsOpen binClosed binTumbler binCompost machineHow to Make a Compost Bin: DIY IdeasWorm Composting (Vermicomposting)Trench CompostingHow to Use Compost for Home GardeningChoose Green Living and Start CompostingClearing Your Doubts About Composting (FAQ)What is the Easiest Way to Compost?Can Meat Be Composted?Is it Better to Compost in the Sun or Shade?
What is Composting, in Simple Words?

Composting is basically recycling for food scraps and plants. You toss in stuff like fruit peels, veggie leftovers, and yard waste, and over time, it breaks down into super nutritious dirt that’s awesome for helping plants grow.
Compost Meaning
When the organic matter decomposes, it becomes a valuable fertilizer that looks like dirt but is extremely nutrient-rich. This valuable fertilizer is called compost. Farmers and green thumbs lovingly call it ‘black gold’ as it enriches the soil and is extremely useful forgardening, agriculture, and horticulture.

Image credit:sorich.in
Why You Should Consider Composting of Waste: A Bouquet of Benefits
Apart from giving you a valuable fertilizer, composting has other vital perks. Here are some of them:
Reduces Methane Emissions

Image credit:wallpaperflare.com
Food scraps and yard residue are major components of our daily waste. When they end up in landfills, wasted food can generate powerful greenhouse gasses like methane that negatively impact the environment.
According to theU. S. Environmental Protection Agency(EPA), wasted food causes 58% of methane emissions from public landfills. However, using food scraps and yard residue for composting can help reduce methane emissions and personal food waste.
Enriches Soil and Lessens Erosion

Image credit:Eva Bronzini
Compost contains three essential nutrients: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. They are vital for the healthy growth of garden plants. Using compost is much better than opting for chemical fertilizers, ascompost improves the soil’s healthand the crop’s productivity. It can also break the compacted soil and improve the soil structure, reducing the risk of erosion.
Conserves Water

Image credit:kaarelp2rtel
TheJournal of Soil and Water Conservationstates that adding organic matter to the soil can help retain moisture. With compost, gardeners and farmers don’t have to constantly water the plants and crops as compost helps preserve moisture.
What Can You Compost?
The right organic matter or ingredients play a crucial role in composting. So, here is the complete list of what you can and can’t compost. Check it properly before you start composting.
YES ✅
NO ❌
*These organic materials might attract animals.
^Although you shouldn’t compost these organic materials at home, community composting facilities might accept them. Check with your local composting facility in advance.
Source:U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
How to Compost at Home

Composting can be done both outdoors or indoors, depending on the available space, type and amount of waste, and the time you can dedicate to it. When you compost at home, you get all the benefits right on your doorstep. Sounds highly convenient, doesn’t it? Well, if it has piqued your interest, let’s learn how to make compost in your own backyard and enjoy its benefits.
First, it’s important to distinguish that there are two major types of composting for yourbackyard:cold/passive compostingandhot/active composting.
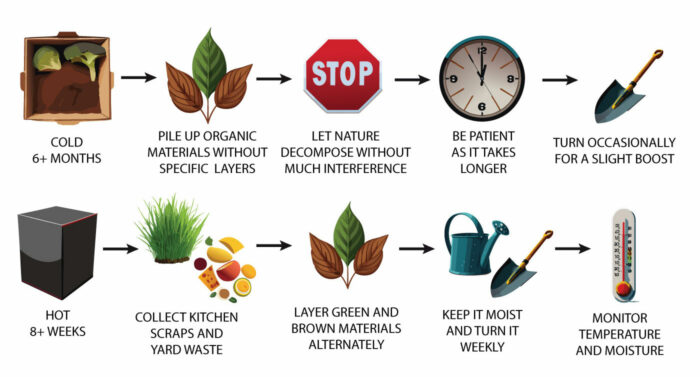
Cold/Passive composting:Cold composting is a slow and primarily anaerobic* process that doesn’t require much effort or maintenance from your end. It’s your go-to process if you have less waste and less time. However, this process might not reach the required temperature to eliminate the pathogens during decomposition. Due to this, your compost might contain some residualharmful pathogens.
*Anaerobic refers to the process where the decomposing organismscan live without airor oxygen.
Hot/Active composting: Hot composting is a faster, controlled, and aerobic* process that requires proper attention and management. It requires the appropriate balance of air, water, carbon, nitrogen, and the right temperature. If everything is balanced correctly, the high temperature willdestroy harmful pathogens, giving you the perfect compost.
*Aerobic refers to the process where the decomposing organismsneed airor oxygen.
Although hot/active composting requires active management, it’s typically faster, kills pathogens and weed seeds, and retains more nutrients. Hence, it’s often considered more advantageous. Thus, let us guide you on how to manage this type of composting:
Compost Ingredients
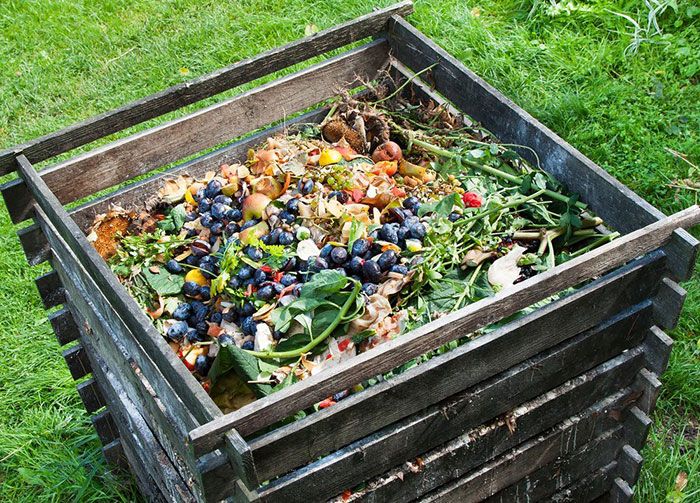

Image credit:Trish Walker
Carbon-rich materials (“browns”), nitrogen-rich materials (“greens”), air (oxygen), and water (moisture)are essential for the decomposing organisms. Carbon is present in all compostable materials. The trick is to balance it with the right nitrogen ratio and an adequate air and water supply; andvoila, the best-quality compost is ready at your fingertips! Two to four parts brown materials to each one part green materials is the perfect carbon-to-nitrogen ratio for your compost pile.

Nitrogen is one of the fundamental and essential elements for the life and development of plants and animals. Fresh organic materials or greens often exhibit a higher nitrogen-to-carbon ratio. The right amount of nitrogen in your home compost pile will ensure faster growth and reproduction of the decomposers. Some household greens include fruit or vegetable scraps or coffee grounds. Use a closed container to store them in yourkitchen.

Note:Too many greens might create a slimy and stinky pile. To avoid that, don’t go beyond the recommended ratio.
Carbon is the essential food that keeps the decomposers alive while they do their work. Brown plant materials exhibit a higher percentage of carbon. Some common browns include dry leaves, twigs, and branches. You can keep an area outside to store them.

Image credit:SuSanA Secretariat, CC BY 2.0 DEED
Consistent aeration will create an aerobic environment for the decomposers to work quickly. For an ideal air flow, ensure all the materials are broken or chopped into small pieces and layered into a pile that you turn regularly. During summers, turn your pile at least once a week. Come winter, you can reduce it to once every three or four weeks. Aeration also helps in reducing the odor.
Ensure your pile is as wet as a wrung-out sponge to maintain moisture. In case of a dry pile, you can add a little bit of water. However, if the pile gets too wet, it might create an anaerobic environment for the decomposers, slowing the process. In that case, just add carbon-rich browns.
Temperature

Image credit:pxhere.com
When the materials decompose, the compost pile’s temperature will rise, particularly at the center. The temperatures of a well-maintained pile can peak up to 130° to 160°F. High temperatures accelerate the aerobic composting process and kill lingering pathogens or weed seeds. If the pile’s temperature doesn’t rise, add some greens and turn the pile.
Size and Location
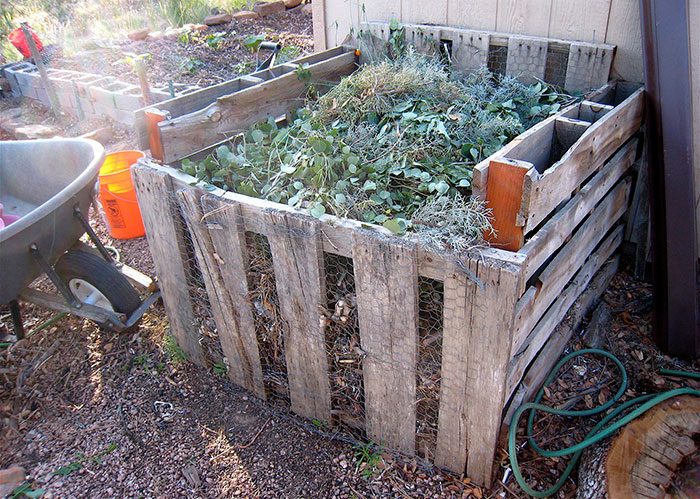

Image credit:Alan Levine
A 3-foot cube is a perfect size for a backyard pile. The central decomposers won’t get enough air if the pile exceeds five cubic feet. Your compost location should be dry and shady with good drainage so it doesn’t get too soggy during monsoons. The shaded spot will keep the pile from getting too dry during summer, so you don’t have to water it constantly. A spot with direct sunlight during winter is also ideal.
Steps for Backyard Composting

Image credit:Maja Dumat, CC BY 2.0 DEED
Step 1:Build or buy a compost bin and determine its location.


Step 3:Start layering your greens and browns in the right ratio (the volume of browns should be twice or thrice for each volume of greens). Keep the food scraps covered and buried with around eight inches of browns.

Step 4:Examine the pile for maintained moisture, aeration, temperature, and odor. Make adjustments and additions as necessary.

Step 5:Occasionally, turn and mix your compost pile to speed up the decomposition.

Step 6:Mixing or turning will no longer heat the pile after a while. When food scraps are no longer visible, let your pile cure or finish. Curing might take more than four weeks. After curing, the pile will reduce to one-third of its initial size.

Step 7:A properly maintained pile will turn into finished, ready-to-use compost in about three months. Sometimes, it might take longer than that. It should smell and look like fresh soil. However, if you notice any materials that didn’t break down, sift the finished compost.

Note:Ensure your pile is safe from flies, pests, and rodents. Use fly traps to protect your indoor compost pile. Maintaining the balance of browns, greens, air, and moisture will keep deterring most pests. To prevent animals from accessing the pile, use a lid and a floor, and avoid adding meat, dairy products, or greasy food.
Types of Compost Bins
You can pick the right compost bin depending on the amount and type of organic material you intend to compost, as well as the space available. Here are the most common types of compost bins:
Open bin

Closed bin
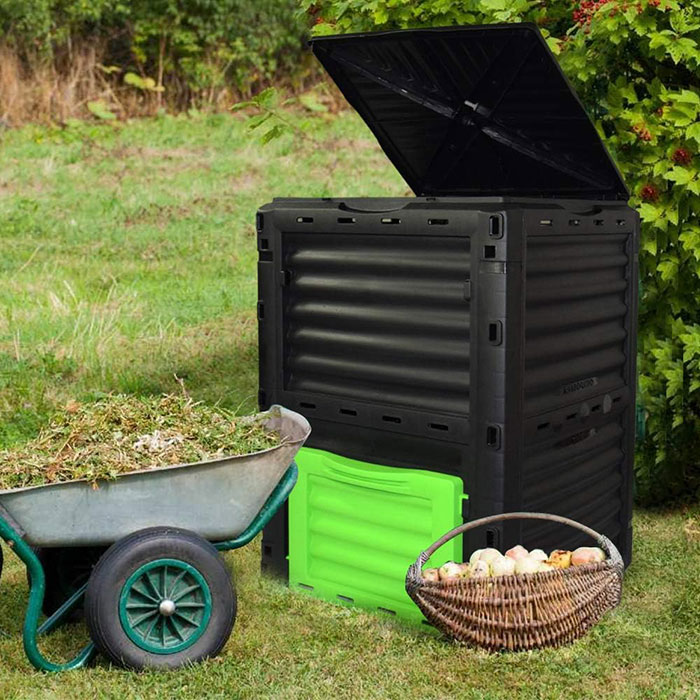

Tumbler bin
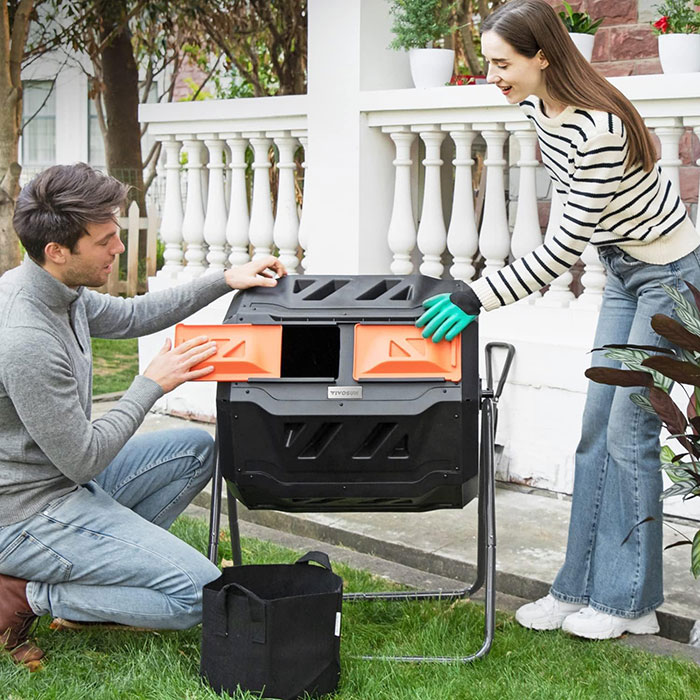

Buy VIVOSUN’s Outdoor Tumbler Compost Bin
Compost machine
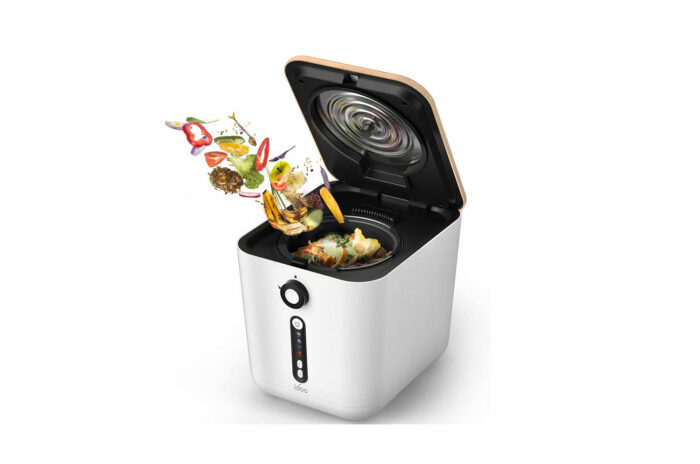

Buy iDOO Electric Compost Machine
How to Make a Compost Bin: DIY Ideas
If you are looking for cheaper bin options for composting, here are a fewDIY hacksyou can try!
DIY Idea #1.Upcycle your old products like garbage cans, wine crates, plastic bins, and wooden dresser drawers into compost bins. Ensure you drill proper holes for airflow and drainage. However, the holes should not be so large that rodents can enter the bin!

Image credit:homemadecatalog
DIY Idea #2.Using wooden pallets, you can create an affordable bin for permanent composting. Use hardware to keep the pallets together. You can make it close or open and use it for hot or cold composting.
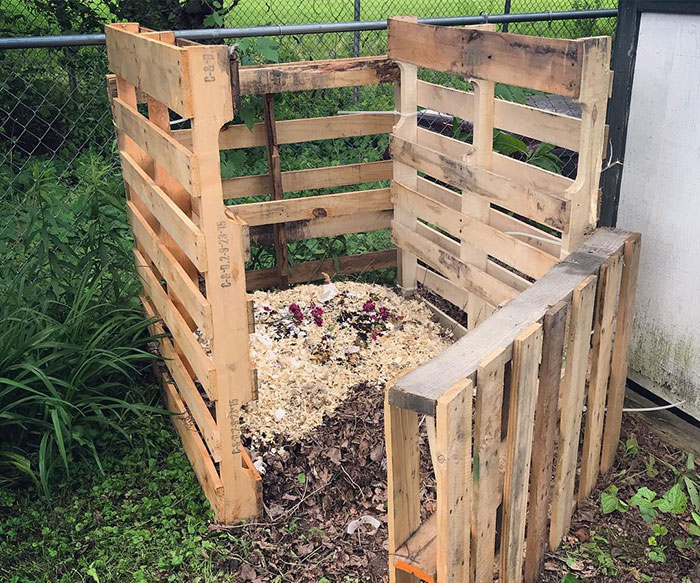

Image credit:beckches
DIY Idea #3.Another budget-friendly option is to drive wooden posts into the soil and wrap the posts using wire fencing. Depending on the amount of compost, you can always change the size of this open compost bin.
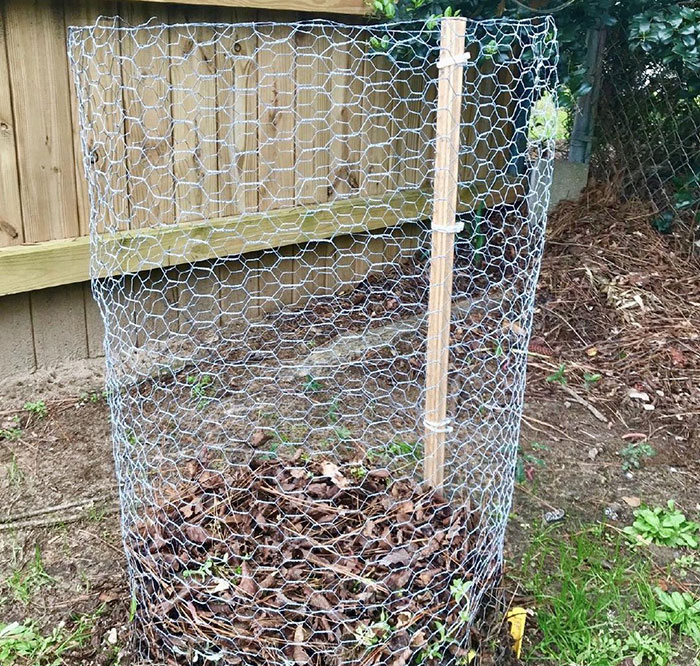

Image credit:makerscorners
Worm Composting (Vermicomposting)

Worm composting,akavermicomposting, is another composting process that works indoors or outdoors. This process requires low maintenance and, when done properly, gives a nutrient-rich vermicompost.
It requires bedding material (dry leaves, straw, shredded paper, or shredded cardboard), worms, food scraps, and, of course, a bin. You can either build your own bin or buy one. Here are the steps for vermicomposting:
Step 1:Determine its location after you build or buy a bin. If you keep it outdoors, keep it warm with blankets during winter. The worms thrive in temperatures 59° to 77°F. However, if you give them a minimum of four inches of bedding, they can endure temperatures from 32° to 95°F.

Step 2:Once you place the bin at the fixed location, start with the bedding. Take dry leaves, non-glossy paper, or cardboard and shred them. Soak these materials for ten minutes, then wring them out. It should feel like a moist sponge. Fill the bin almost halfway with this moist bedding and top it with a fistful of soil.
Step 3:Purchase ‘red wriggler’ worms (Eisenia fetida), which are ideal for vermicomposting. Initially, place around 1000 worms on the bedding.

Step 4:Give some time (a day or two) for the worms to settle into the new environment. Then, you can start feeding them with small amounts of fruit and vegetable scraps, crushed egg shells, coffee grounds, paper filters, and paper tea bags (remove the staples). Don’t feed them citrus fruits, greasy or odorous food, dairy products, pet waste, or bones.

Step 5:Cover the food scraps with two inches of bedding every time.

Step 6:Once the worms start reproducing, you can increase their feeding amount. However, ensure they have eaten the previous food scraps before giving them new food.

Step 7:You can harvest the vermicompost within three to six months and use it immediately, as it doesn’t require curing.

Trench Composting
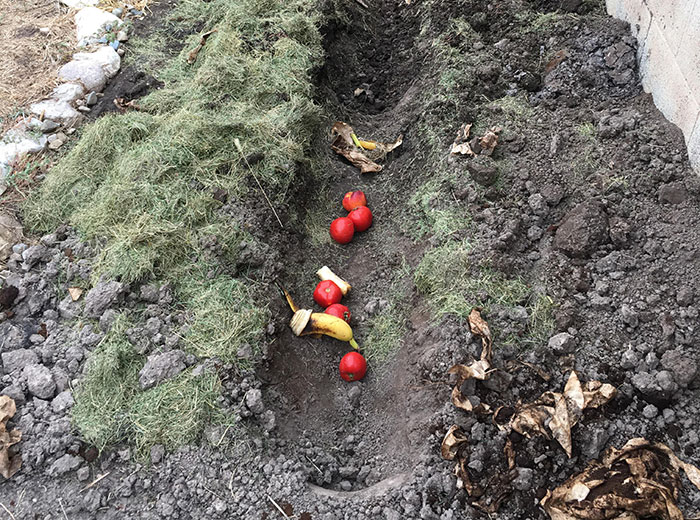

Image credit:EcoDruid

As the waste is underground, it doesn’t stink. You can do trench composting any time of the year, provided that the soil remains manageable. As you bury the waste deep under the ground, you can even compost small volumes of cooked food waste like meat, grains, and dairy products. Unlike the other composting methods, this one is unlikely to attract animals and insects.
Here are the easy steps to start trench composting today:
Step 1:You can’t harvest the end product in trench composting. So, pick a spot where you want the nutrients to enrich the soil. Avoid digging next to established root systems, as this could harm plants that grow there.

Step 2:After choosing an ideal location, take a shovel and dig an elongated hole of around 12 to 24 inches.

Step 3:Ensure your organic waste is moist enough and place it in the hole.

Step 4:Cover the hole back with the soil and mark the spot so you won’t compost there again.


Note:Like all cold composting methods, trench composting is slow. It’s not ideal for ongoing composting as it requires digging your yard regularly. It also takes up a lot of space as you can’t compost in the same spot twice. Moreover, you can’t plant anything above the trench top as the soil sinks during decomposing.
How to Use Compost for Home Gardening

Image credit:WhyIIzHere
Unfinished compost can potentially damage the plants and attract pests and animals. Only cured compost, which is finished and ready for use, ensures optimal benefits. Finished compost will be crumbly and look and smell like fresh soil with a dark and rich color. Here’s how you can use it:
Note:Old compost might lose some nutrients. However, compost can never go “bad.”
Choose Green Living and Start Composting

Image credit:mindfulofmango
See, composting isn’t as difficult as you thought, is it? We hope you had fun learning what composting is, how to compost at home, and discovering the multiple ways to do it. Whether you are an environmentalist or a green thumb who enjoys organic gardening, we hope this guide made your mind a little clearer, your life a little greener, and your heart a little happier! So, are you ready to make this black gold?
Clearing Your Doubts About Composting (FAQ)
What is the Easiest Way to Compost?
Cold composting is the easiest way to compost since it’s so low maintenance, but it’s got its downsides. It tends to retain harmful pathogens and is extremely slow.
Can Meat Be Composted?
Meat can be composted in trench composting as it gets buried underground. However, avoid composting it in an outdoor bin as it might attract insects and animals.
Is it Better to Compost in the Sun or Shade?
You can keep a regular compost bin in the sun. Just ensure to add a little water if it gets too dry. Moreover, if you live in a hot region, you can build a shade over the compost bin so it receives indirect light. Shaded spots are better for worms and vermicompost bins.
2Kviews2Kviews
You May LikePeople Are Sharing Their Decked-Out Bedrooms, And Here Are 30 Of The Most Amazing OnesŽydrūnė Trukanavičiūtė32 Game Room Ideas to Turn Your Gaming Cave Dream into RealityAivaras KaziukonisCandle Magic: Transform Your Home with a Candle WarmerEligijus Sinkunas
Žydrūnė Trukanavičiūtė
Aivaras Kaziukonis
Eligijus Sinkunas
Home & Design