The early bird catches the worm, just like their ancestors, the Neanderthals, did.
You read that right: new research suggests that people who go to bed early and wake up early are likely to share the same DNA as the extinct species of archaic humans.
The University of California in San Francisco came out with a study published on Thursday (December 14) in the journalGenome Biology and Evolutionthat compared genes related to early rising from people alive today and DNA from Neanderthals and Denisovans to spot the pattern.
HighlightsEarly risers may share DNA with Neanderthals and Denisovans.Research uses UK database of genetic, health, lifestyle info.Neanderthal genes may reflect adaptation to northern latitudes.
New research suggests people who go to bed early and wake up early are likely to share the same DNA as Neanderthals
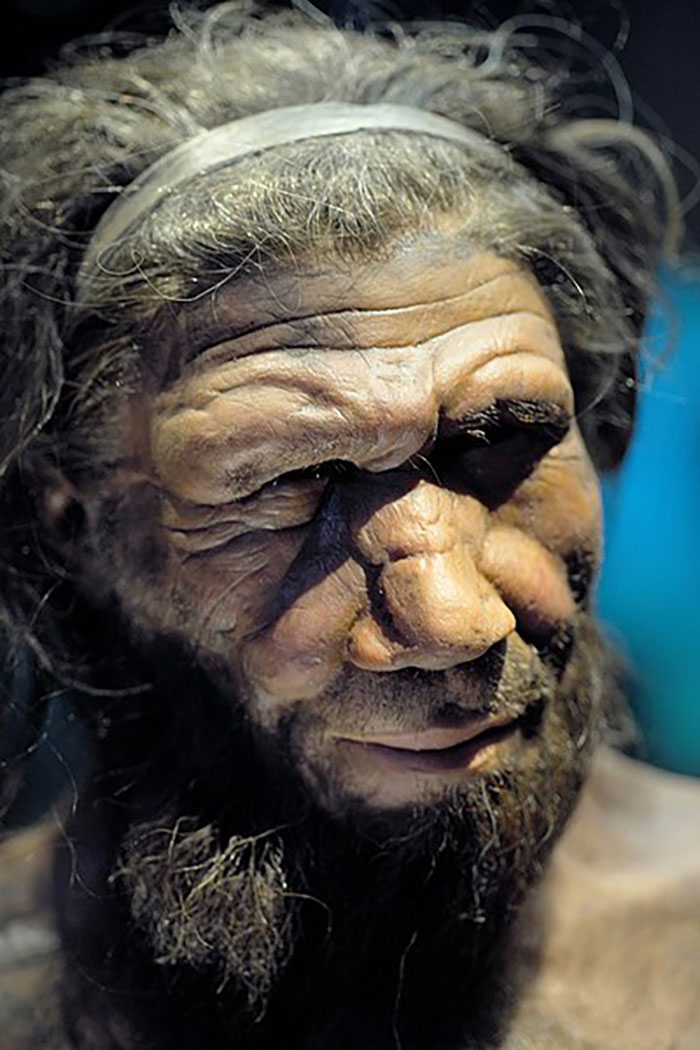

Image credits:Werner Ustorf
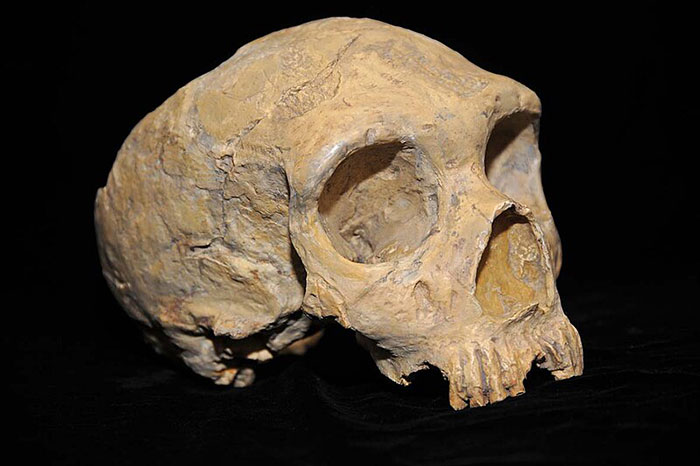

Image credits:AquilaGib
The Denisovans, like the Neanderthals, are also an extinct subspecies of archaic humans that lived during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic.
By using a UK-based database that holds genetic, health, and lifestyle information on half a million people, it found those with the same early-rising variants as Neanderthals had self-reported their preference for waking up early, theIndependentreported.
“We’ve found many Neanderthal variants that consistently associate with a propensity for being a morning person”, an evolutionary geneticist said

Image credits:yanalya

Image credits:Andrea Piacquadio
Tony Capra, an evolutionary geneticist at the University of California, San Francisco said: “We’ve found many Neanderthal variants that consistently associate with a propensity for being a morning person.
Tony reportedly explained that many modern humans probably carry the Neanderthal gene because it helped their ancestors adapt to life at higher latitudes in northern Europe.
He further explained: “We don’t think that being a morning person is actually what was beneficial. Rather, we think it is a signal of having a faster running clock that is better able to adapt to seasonal variations in light levels.
Neanderthal DNA may play a small role in swaying the course of Covid-19 infection
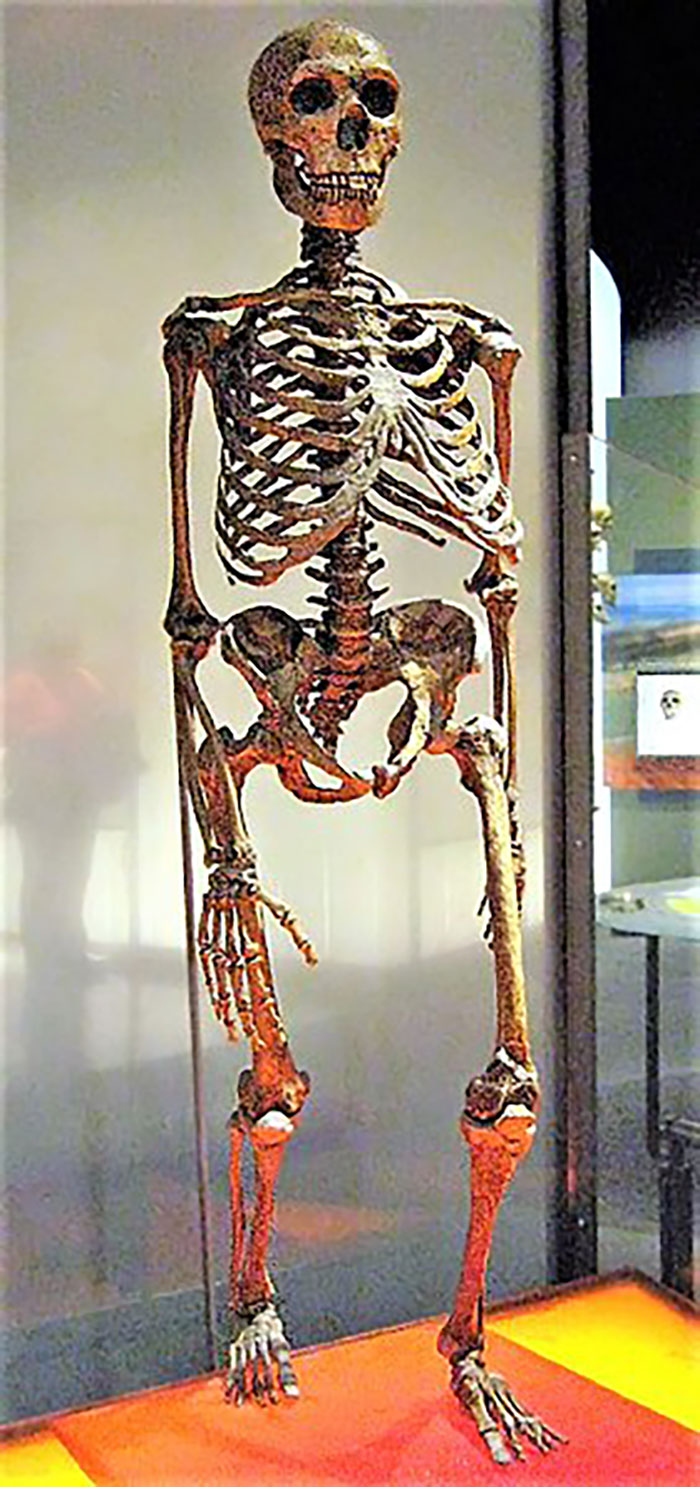
Image credits:Claire Houck
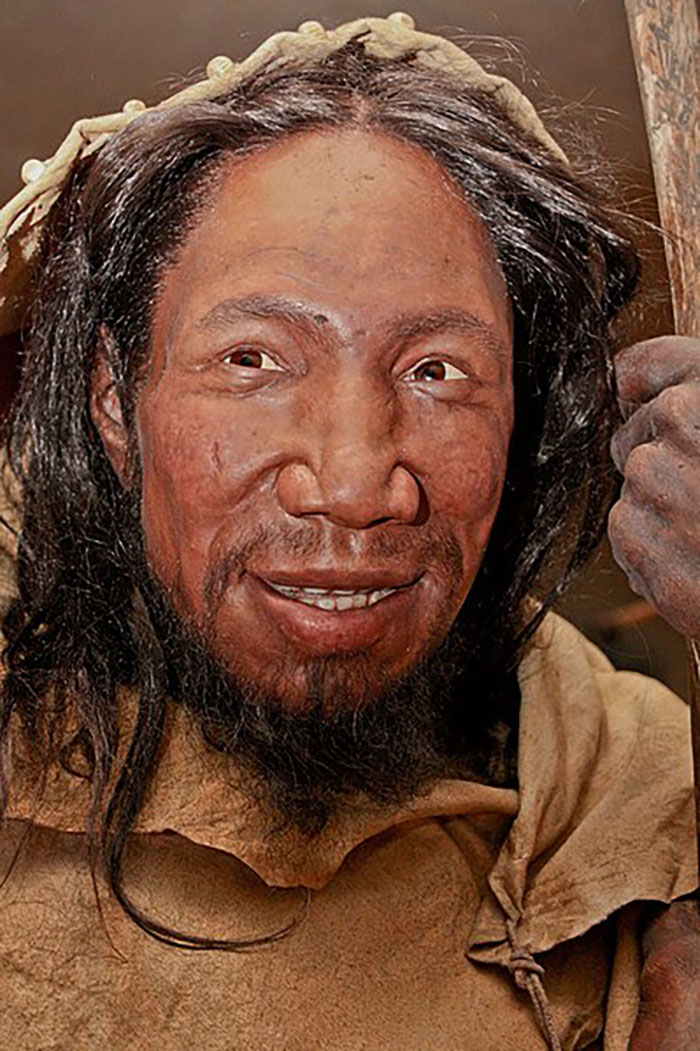

Image credits:Daniela Hitzemann
“At higher latitudes, it is beneficial to have a clock that is more flexible and better able to change to match the variable seasonal light levels.”
Professor Mark Maslin, of University College London, who was not involved in the study, told the Guardian: “Now we have genetic evidence that some of us really are morning people.
“When humans evolved in tropical Africa, the day lengths were on average 12 hours long. Now hunter-gatherers spend only 30% of their awake time collecting food, so 12 hours is loads of time.
Scientists have been studying the genetic differences between archaic and modern humans since 2010
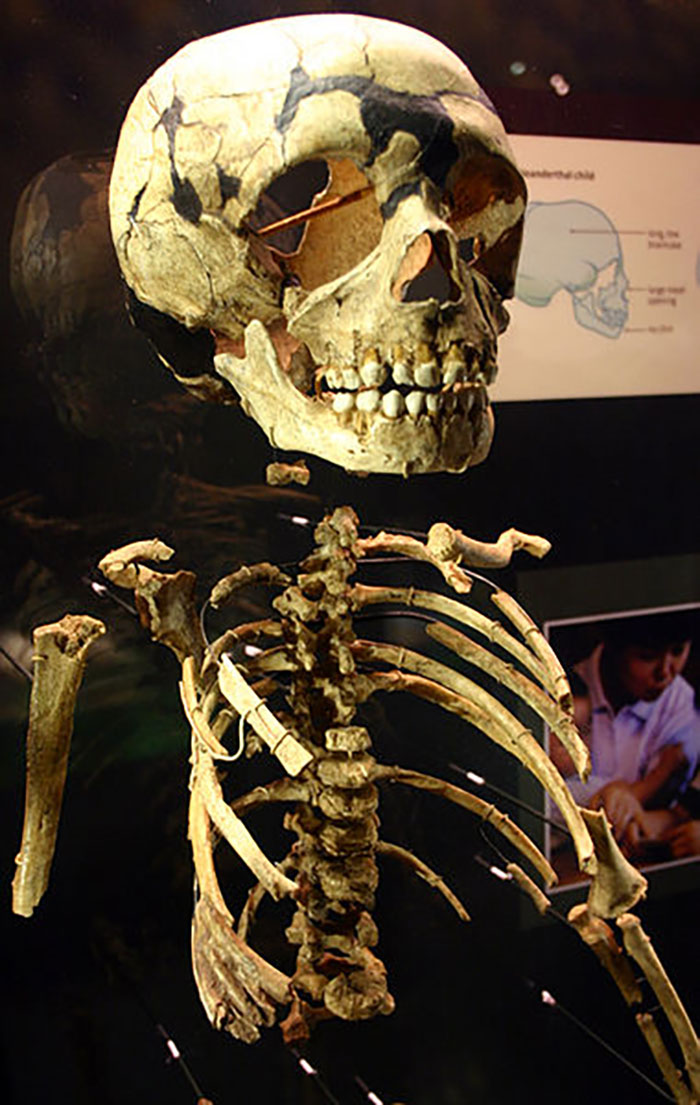
Image credits:Ryan Somma
Scientists have been studying the genetic differences between archaic and modern humans since 2010, when the Neanderthal genome was sequenced for the first time, as perCNN.
The same year, genetic sequencing of ancient DNA from a fossil also revealed the Denisovans, which were unknown prior to that time, the American broadcaster reported.
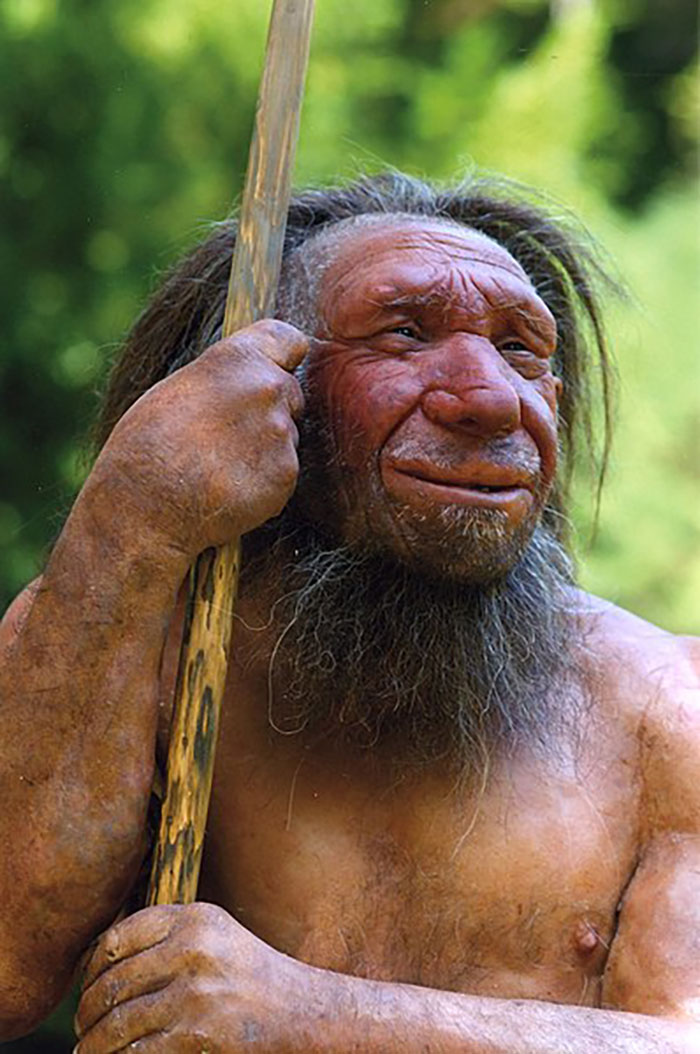

Image credits:Neanderthal-Museum, Mettmann
Moreover, Neanderthal DNA may play a small role in swaying the course of Covid-19 infection, research has found, and a study published in June reported a link between Neanderthal DNA and Duputytren’s disease, an abnormal thickening of tissue in the hand.
According toScience Focus, we aren’t sure when the Denisovans died out, with limited DNA evidence even suggesting they may have survived in New Guinea or its surrounding islands until 15,000-30,000 years ago.
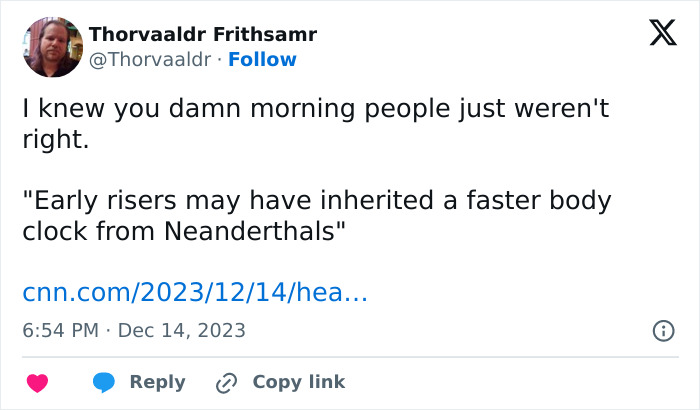
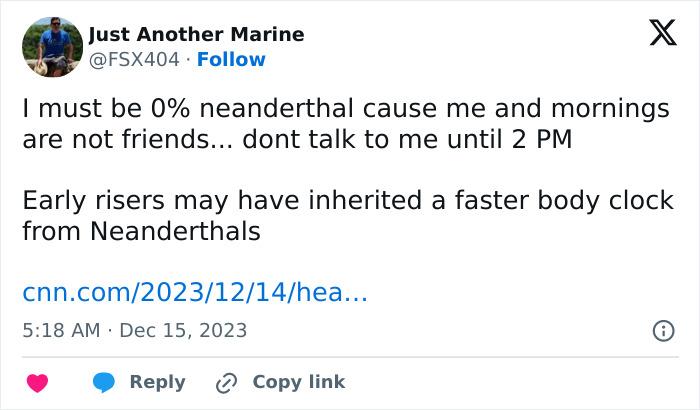
People had funny reactions to the new research





Thanks! Check out the results:Lei RV
Renan Duarte
News